Not sure of a term we referenced? We break down all the various internet definitions you may encounter when learning about broadband service. We’ve also included commonly used acronyms and added in-depth explanations for the more complex terms that are helpful to understand when buying internet.
On this page:
The importance of digital literacy and the internet
6 ways digital literacy can improve your life
Numbers and symbols
302: HTTP status code for found and is used to temporarily redirect visitors
400: HTTP status code for bad request
401: HTTP status code for unauthorized access
403: HTTP status code for forbidden access
404: HTTP status code for error or page not found
500: HTTP code for any unexpected error
502: HTTP code for bad gateway server error response
503: HTTP code for service unavailable
504: HTTP code for gateway timeout
Internet glossary puzzles

Note: To print the game, download here. Answers are available at the bottom of this article.

Note: To print the game, download here. Answers are available at the bottom of this article.
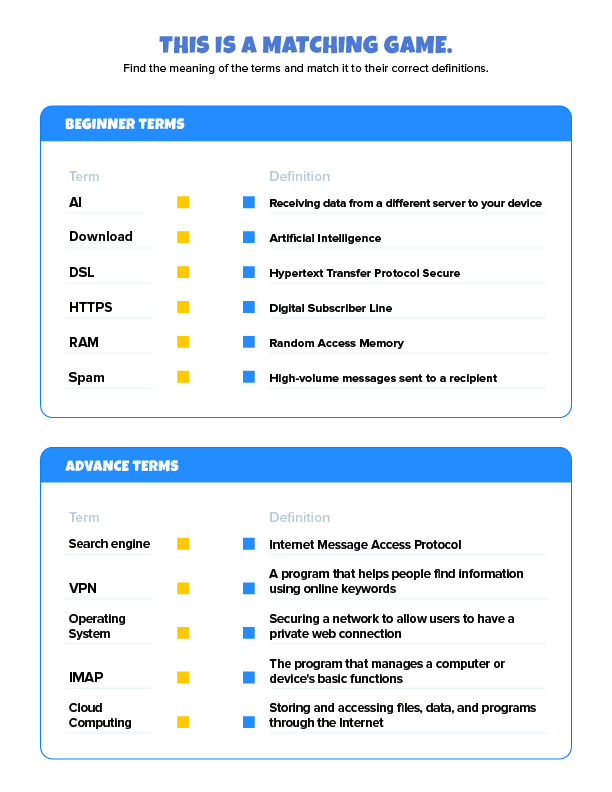
Note: To print the game, download here. Answers are available at the bottom of this article.
Internet terms glossary
A
AI: Artificial intelligence (machines performing tasks that normally require human intelligence).
Algorithm: A procedure for solving computer science problems.
Anti-malware: A type of software program that helps prevent computers and other technology from malicious software (known as malware).
Anti-spyware: A type of software program designed to remove spyware, which is software that spies on a user’s computer activities.
Anti-virus: A type of software that eliminates computer viruses.
B
Bandwidth: Bandwidth measures the total number of frequencies, or capacity, a network connection can handle at any given moment. With more bandwidth, more data can be transferred through a specific network at a time. This is significant for determining how many devices can connect to the network simultaneously.
Bluetooth: A short-range wireless interconnection between electronic devices.
Broadband: Broadband tells you how quickly data can be transferred, which is your overall measurement for the speed of your internet connection. This is significant for determining the speed at which your internet can perform certain tasks, such as streaming a movie.
C
Cable internet: An internet service type that uses coaxial cables to transmit data.
Cache/caching: Stored data through a software component for that data to be accessed more efficiently in the future.
Capping: Also known as data capping. When you have a limit on how much data you can use in a month.
Cloud computing: Data storage centers available over the internet.
Cookies: Data stored in a text file that’s used to identify a user’s computer.
D
Data cap: A monthly limit on the amount of data a user is allowed to use when accessing the internet
Dial-up internet: A type of internet service that works by taking over the signal of an existing phone line and changing it from communicating voice to communicating data.
Download: Receiving data from a server onto one’s electronic device.
Download speeds: The speed it takes to download data from a server in the form of images, videos, text, files and audio. This is the type of speed most people think of when they think of internet speeds.
DSL: Digital Subscriber Line is a type of internet service that utilizes telephone lines to transmit data.
E
E-commerce: Short for electronic commerce. The buying and selling of goods via the internet.
Encryption: Converting data into code for privacy purposes.
Ethernet: A way to connect computers to a Wi-Fi network through a wired connection.
Extender: Short for a Wi-Fi extender. A device that connects with your router (either wirelessly or through a wired connection) to help extend your internet signal into rooms that are Wi-Fi dead zones due to walls, furniture obstructions or general spacing.
F
FCC: Federal Communications Commission. An independent agency of the U.S. government responsible for implementing and enforcing America’s communications laws and regulations.
Fiber internet: A type of internet service that utilizes fiber optic cables to transmit data.
Firewall: A network security system that blocks unauthorized access and controls outgoing and incoming communication with predetermined security rules.
FTP: File Transfer Protocol. The protocols computers follow to transfer files from one system to another.
G
Gigabit: A unit of measurement equivalent to 1,000 Mbps.
Gigabit broadband: Internet speeds of up to 1 Gigabit. These speeds are some of the fastest available.
H
High-speed internet: The FCC defines high-speed internet as 25 Mbps download speeds and 3 upload speeds, but this definition will likely increase in speed as technology advances.
HTTP vs HTTPS: The beginning of a website URL and the protocol used to transfer data over the web. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is more common but HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is more secure because it uses encryption.
I
IMAP: Internet Message Access Protocol. Standard email protocol that stores email messages onto a mail server.
Internet of things: Physical objects, such as smart home security systems, that can collect and transfer data over a wireless network without any human interference.
IP Address: Refers to the unique string of numbers that identifies your devices. The IP address is commonly referred to as the ZIP codes of the internet.
ISP: Internet Service Provider. A company that provides internet services.
J
Jitter: Small intermittent delays during data transfers.
K
KB/KBPS: Kilobit or Kilobit per second is a measure of data transfer speed. 1,000 KBPS equals 1 Mbps, which is the typical form of measurement for internet speed.
L
Latency: Latency measures the delay in data transfer, telling you how fast data gets from a source to its destination.
Link: Short for hyperlink. When a user can click on a highlighted section and be transferred to a new website
Log in: How users access their account.
LTE: Long-Term Evolution. The broadband standard for wireless devices. The most common mobile broadband standard is currently 4G LTE.
M
Malware: Also known as malicious software. Software that is specifically designed to disrupt, damage or gain unauthorized access to a computer system.
Megabyte: A unit of measurement. Internet speeds are typically measured in megabytes per second.
Mesh Wi-Fi: A group of devices throughout a home that acts as a single Wi-Fi network. Each device is called a point and the purpose of having multiple points is to provide better coverage for more areas of the house.
Mobile broadband: Another term for wireless internet access, which means internet access delivered over a mobile network.
Modem: A modem receives signals from your internet service provider and translates them for your devices to use.
MP3: A stored audio file (only able to store audio and images).
MP4: A stored multimedia file (able to store video, stills, subtitles or text).
N
Net neutrality: The principle that ISPs should provide all online content equally without favoring or blocking specific products, websites or types of content.
Network: Two or more computers (or other devices) are linked to share resources. This can mean a Wi-Fi network or even just the internet.
O
Operating System: The software that manages a computer’s basic functions.
OSS: Open Source Software. When the copyright holder of software grants users the ability to use, modify or distribute the software through licensing agreements.
P
Phishing: A form of fraud where someone pretends to be someone else online to acquire personal information from another person or to deploy malware onto the victim’s computer or another device.
Ping: A ping is a test that determines if a server is reachable. The test sends a data packet to the server to see if the data comes back.
Piracy: The unauthorized use, copying or distribution of something that has been copyrighted.
POP3: Post Office Protocol is a protocol used by email users to receive emails by downloading them to a computer from a mailbox of a server.
R
RAM: Random access memory is short-term computer memory where working data is stored. Since it is short-term, it is not stored on a computer’s hard drive.
Remote desktop: A centralized server that allows users to access their profiles on a separate device.
Router: Takes the internet signals provided by a modem and converts them into a Wi-Fi signal so that devices can connect to the internet wirelessly.
S
Satellite internet: An internet service type that relies on satellites to transmit data into the home.
Search engine: A program that allows users to search for information in a database. The most well-known search engine is Google.
SIM: A Subscriber Identification Module is a card inserted into a mobile device that securely stores personal data, including an international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number.
Spam: Unsolicited messages over the internet received by a high volume of recipients.
Spyware: Software that allows someone to covertly obtain information regarding another person’s computer activities.
Static IP: When the IP address stays the same over time.
Streaming: Media content available for immediate watching or listening via any electronic device over the internet.
T
Throttling: When your internet provider limits your bandwidth or slows your connection to certain online activities after you’ve reached a monthly limit.
Traffic: The flow of data within an internet network.
Trojan Horse: Malware that downloads to a computer disguised as legitimate software.
U
Ultrafast: Internet access with exceptionally fast speeds.
Unique user: An IP address, plus a further identifier.
Unlimited: When there are no data caps for internet use.
Uploading: Sending information from your computer to another device or server on the internet. Common examples include email, Zoom and live gaming.
Upload speeds: This tells you how quickly information from your network is sent to external networks.
V
Virus: A malicious piece of code designed to steal data from a device or damage the device entirely.
VOIP: A Voice over Internet Protocol is a technology that allows a user to make voice communications over the internet instead of through a phone line.
VPN: A Virtual Private Network is a secure connection method that allows verified users to connect to a private network that has been extended across a public network.
W
WAN: A Wide Area Network is when multiple networks communicate with one another (a network of networks). The internet is the world’s largest WAN.
Wearable: Smart electronic devices you can physically wear
Web browser: Any application software that can access the World Wide Web (Chrome, Safari, Firefox, etc.)
Wi-Fi: Short for wireless fidelity and is the technology that allows your devices to wirelessly connect to the internet.
WLAN: A Wireless Local Area Network is a network of two or more devices that can connect to the internet wirelessly and exist near each other (a home, school, library, etc.).
X
XML: Extensible Markup Language is sets of codes or tags that describe the text in a document (ex: HTML).
Z
Zip file: A file format that compresses one or more documents into a single zip file.

The importance of digital literacy and the internet
The American Library Association defines digital literacy as “the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate information, requiring both cognitive and technical skills.”
Digital literacy includes something most of us do daily: the ability to check and read our emails on a digital device like our cellphone or tablet.
Digital literacy is also the ability to conduct online research to learn more about a subject, either for personal knowledge, work or school.
Simply using a search engine to discover an answer to a question or creating a profile of yourself on a social media account are examples of your digital literacy.
According to Statista, over 90% of Americans have internet access. The internet has proven to be an invaluable tool in our daily lives, especially since the onset of the worldwide pandemic in 2020 drove our workplace, educational institutions, grocery stores and even our medical offices online.
Digital literacy is important for all stages of our lives, from young students attending school virtually to older computer users accessing their doctor or staying in touch with family.
6 reasons why digital literacy can improve your life
1. Making connections with family and friends
Being social is in a human’s nature and staying in touch with our family and friends can benefit our mental health. In fact, “social media has become a source of internal healing for a lot of senior citizens battling depression,” according to the Miami Home Care Services.
2. Increased safety
With digital literacy comes understanding good online safety practices that can help to increase your safety – from protected passwords to recognizing signs of spam.
3. Save time
Being digitally literate can save you time, whether you have an online appointment call with your doctor, do your shopping online or take a virtual class. Think of all the time you save by not driving, standing in line, etc.
4. Supports lifelong skills
Nearly everything we do requires some level of digital literacy. Many companies require an online application or an emailed resume to apply for open positions. Our patient portals are online, as are many government assistance agencies.
5. Helps educational progress
Not only will digital literacy help your student with research and social skills, but it will also allow them to learn how to stay safe online.
Post-pandemic, many educational institutions have adopted a hybrid approach to education, with most classes being held in person, but some assignments and classes are still accessible online. Parents can often access their student’s classroom portal and keep track of grades and assignments, as well as handle communications with educators.
6. Close the digital divide
Access to technology in our post-pandemic world is essential. However, there is still a digital divide in the U.S., mostly in rural areas, but also in pockets of urban areas.
The digital divide is the division between individuals who have access to computers and high-speed internet and those who do not.
For students, this is particularly worrisome, as they risk falling behind their classmates. According to a Pew Research Center survey, “24% of teens living in lower-income households often or sometimes are unable to complete homework due to lack of reliable computer or internet access.”
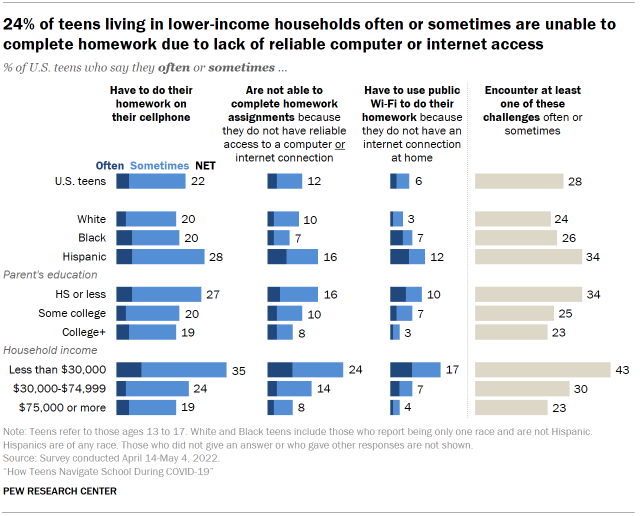
To combat the digital divide, the federal government has implemented the Affordable Connectivity Program, which partners with internet service providers to offer high-speed internet plans for $30/mo., which will allow anyone qualified to receive the $30/mo. stipend from the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) to get internet service for free.
See puzzle answers here.
Allconnect: Let us compare providers for you
Why should you choose Allconnect? We’re the #1 broadband marketplace in the U.S, meaning you can trust us to search, compare and order internet and TV service for your home.
Get started

Written by:
Ari HowardAssociate Writer, Broadband & Wireless Content
Ari Howard is a staff writer Healthline and spent two years as a writer on the Allconnect team. She specialized in broadband news and studies, particularly relating to internet access, digital safety, broadband-…
Read more
Edited by:
Robin LaytonEditor, Broadband Content
-
Featured
![How to lower your internet bill]() How to lower your internet bill Camryn Smith — 6 min read
How to lower your internet bill Camryn Smith — 6 min read -
Featured
![Understand speed test results and learn to boost your internet speed]() Understand speed test results and learn to boost your internet speed Samantha Cossick — 6 min read
Understand speed test results and learn to boost your internet speed Samantha Cossick — 6 min read -
Featured
![18 tips to improve your internet connection and boost Wi-Fi signal]() 18 tips to improve your internet connection and boost Wi-Fi signal Camryn Smith — 9 min read
18 tips to improve your internet connection and boost Wi-Fi signal Camryn Smith — 9 min read
Latest
-
Thursday, July 25, 2024
Worried about losing your signal? This is how to keep your satellite dish cleanDavid Anders — 6 min read
-
Tuesday, July 23, 2024
The best free TV and movie streaming services 2024Camryn Smith — 5 min read
-
Tuesday, July 23, 2024
Everything you need to know about internet speedsRobin Layton — 8 min read






