Have you had enough of screaming at your Wi-Fi connection for being too slow? Wi-Fi does have a reputation for being slower than an Ethernet cable connection. Wi-Fi can be slow for a number of reasons, including improper router placement, setting issues on the router, internet service provider (ISP) problems and hardware problems.
Is Ethernet faster than Wi-Fi?
To put the concept to the test, we ran a speed test between a Wi-Fi connection and an Ethernet connection. Below are the screenshots from the two speed tests looking at Wi-Fi vs. Ethernet. This test is with T-Mobile’s 5G Home Internet. There’s no set speed tier, but typical speeds are between 33-182 Mbps according to T-Mobile’s website, but we usually get like 300 Mbps.
How much faster can Ethernet speeds be?
Ethernet cables can consistently deliver up to 10 Gbps, whereas Wi-Fi 6E, the latest generation of Wi-Fi connectivity, reaches around 5 to 8 Gbps. An Ethernet cable will give you the most possible speed out of your internet plan.
Latency and security
An Ethernet cable connection solves any latency or speed fluctuation issues you may experience while using Wi-Fi. Also, an Ethernet cable provides you with better security as it is set up to attach a device through the cord to your network, but data on Wi-Fi is traveling across bandwidth that can be accessed by outside parties.
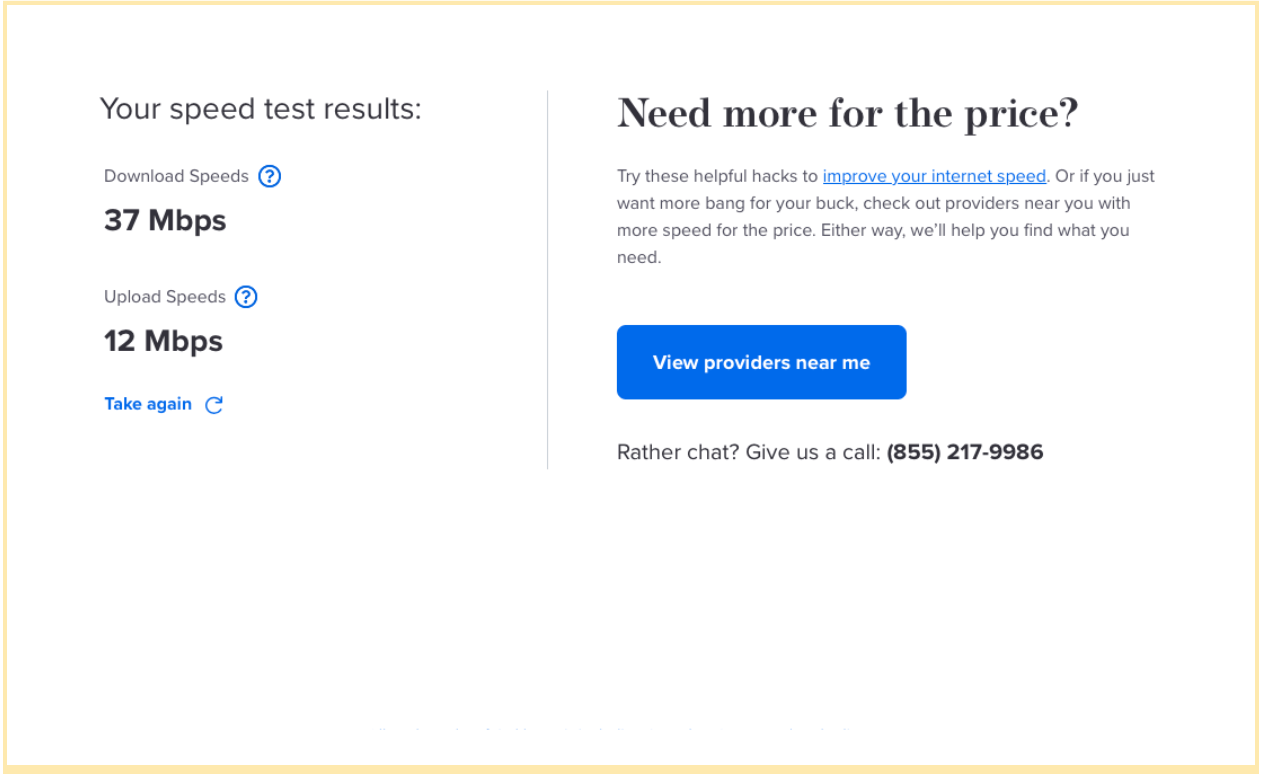
Wi-Fi speed test results:
Ethernet speed test results:
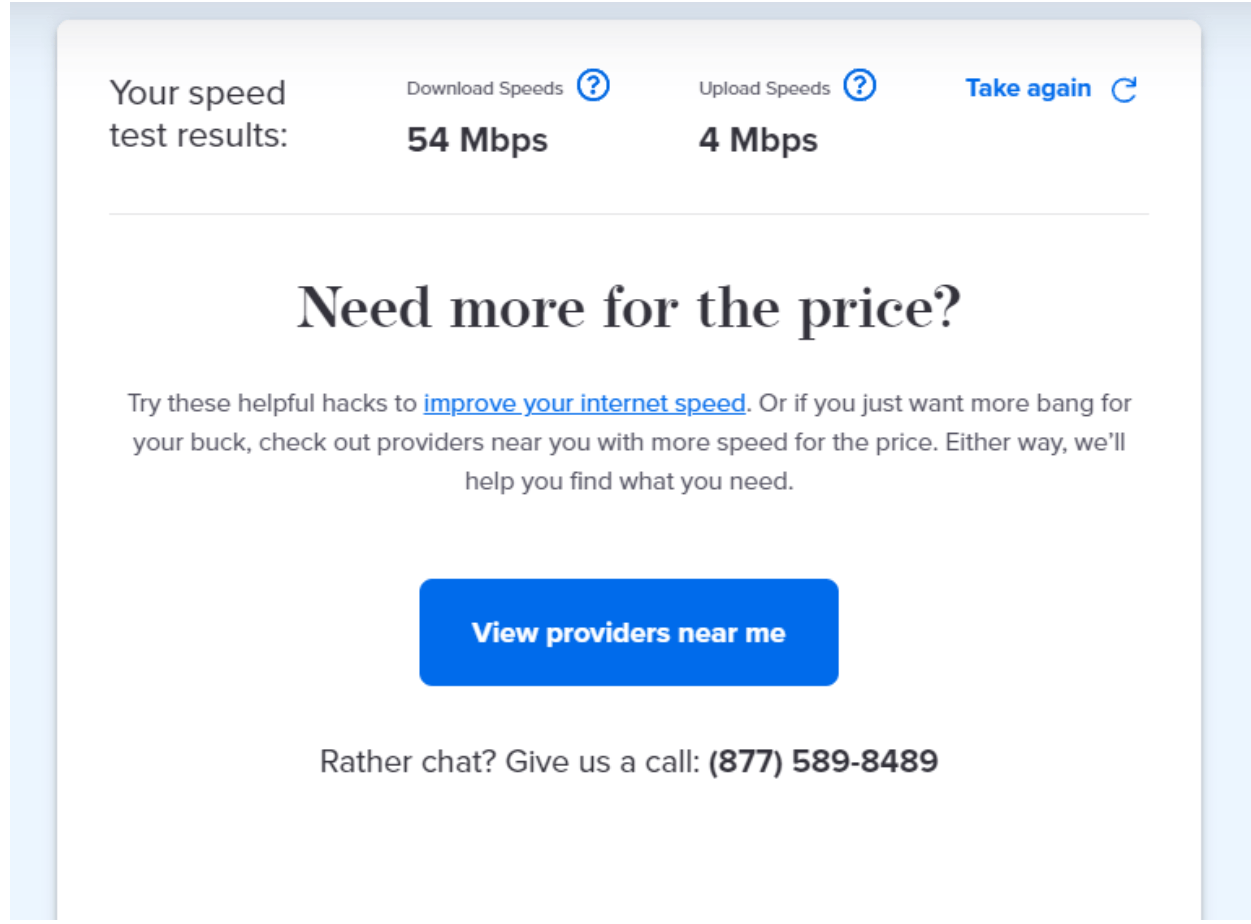
As you can see, the Wi-Fi speed test did come back as slower for download speeds by 17 Mbps compared to the wired Ethernet connection. It’s interesting to note that the upload speeds for Wi-Fi were significantly faster, with 12 Mbps upload speeds for Wi-Fi and 4 Mbps for Ethernet.
However, if you’re streaming or just browsing the internet, download speeds tend to affect the experience more. Meanwhile, upload speeds are important for gaming and video conferencing, since it affects how you sound or look to others.
Below we’ll look at reasons for why Wi-Fi can end up being slower than Ethernet in certain instances.
Router placement can affect Wi-Fi speeds
Wi-Fi is a signal that can travel at greater distances than an Ethernet signal traveling through contained, physical cables. But Wi-Fi is actually a radio signal that goes from the router to the digital device you are using. That means the signal must travel unimpeded about the home for devices to get a strong enough signal.
In another one of our articles, a physicist explained some of the best places to put a router for maximum signal strength. He created a refractive index map showing the best place to put his router in his apartment. Some of the best places to put the router are on a mantel in a central family room, a small coffee table in a central hallway or living area and on the second-floor landing if there is no basement.
There are also places to avoid putting the router, as these can block the signal. These places include the kitchen, where other devices can interfere with the signal, in a corner or windowsill since the signal can travel outside or down in the basement.
Equipment issues might slow speeds
Sometimes resetting the router can also increase speeds. As simple as it sounds, it can be an easy fix.
If you have an older router, that could be the source of the problem. Newer routers can work with a wider array of devices, handle faster speeds, have expanded features for better connectivity and have updated security measures.
The router might also just need some add-ons. You might also look into getting an upgraded antenna or an omnidirectional antenna. These can help boost signals across the home in ways that routers from the ISP alone sometimes cannot. You can also find other additional devices made for boosting your Wi-Fi signal. Wi-Fi repeaters and internet extenders can help you extend the Wi-Fi signal to other areas of the home.
Optimize your settings for faster Wi-Fi
To get the fastest Wi-Fi possible, make sure your Wi-Fi settings are optimized. One of the most important things you can do is to make sure your network is secure so that people are not leeching off your Wi-Fi signal. Make sure your network is secure by using a complex password and WPA2 security.
You can also switch your router from a standard 2.4 GHz channel to a 5 GHz channel to up your speeds.
Routers can also have settings that allow you to prioritize certain devices. Since gaming, streaming and video calls all take a lot of bandwidth, telling the router which devices to prioritize can speed up the most important tasks. Intel gives the example of prioritizing video calls since those could be work-related, over downloading from the cloud, since you could access your files later. See if your router has Quality of Service (QoS) settings to help.
You might also look into presets on the router. For instance, some have entertainment settings that prioritize bandwidth for streaming or gaming. If multiple people are gaming or streaming, the devices end up competing with each other for bandwidth priority. If people tend to use multiple entertainment devices at the same time, you can turn off the entertainment settings, if your router has them.
Issues may come from ISP
Sometimes your internet service might just be bad. If your provider offers slow upload and download speeds, no matter what you do, you won’t be getting speeds faster than your plan allows. If your plan caps at 40 Mbps, then that’s the fastest internet you’re likely to get.
Some ISPs also have data caps, which means if you go over a certain data limit, your ISP can slow down your internet for going over that data cap.
If you find your internet is simply too slow for your surfing, gaming or streaming needs, it might be time to find a new provider if you’re able or possibly switch to a higher data plan with your current ISP.
Wi-Fi vs. Ethernet for gaming
An Ethernet connection is the preferred method for gamers, as it will give you a better and faster experience without any lag, generally called network or variable latency which is the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another.
Using an Ethernet connection while gaming is often more reliable than Wi-Fi simply because your signal isn’t likely to fade in and out.
When you should consider Ethernet over Wi-Fi
Sometimes you can do everything right and Wi-Fi will still end up being slower than Ethernet. Wi-Fi will always be a radio signal that has to travel from the router to the device, whereas Ethernet has a contained cord to travel through.
If lightning-fast internet speeds are a must for uses like gaming, you might consider using Ethernet cables for stationary devices like computers or gaming consoles. Mobile devices like phones, tablets or other wireless devices like smart home gadgets can use the Wi-Fi signal.
Allconnect: Let us compare providers for you
Why should you choose Allconnect? We’re the #1 broadband marketplace in the U.S, meaning you can trust us to search, compare and order internet and TV service for your home.
Get started
Written by:
Michelle Honeyager
Michelle Honeyager is a contributor for the Allconnect team. She has been writing professionally for over 10 years, and covers topics pertaining to home internet tech and internet service. She graduated from Mou…
Read more
Edited by:
Robin LaytonEditor, Broadband Content
-
Featured
![18 tips to improve your internet connection and boost Wi-Fi signal]() 18 tips to improve your internet connection and boost Wi-Fi signal Camryn Smith — 9 min read
18 tips to improve your internet connection and boost Wi-Fi signal Camryn Smith — 9 min read -
Featured
![Ethernet cable speed categories explained]() Ethernet cable speed categories explained Camryn Smith — 5 min read
Ethernet cable speed categories explained Camryn Smith — 5 min read -
Featured
![The best Wi-Fi routers of 2024]() The best Wi-Fi routers of 2024 Camryn Smith — 7 min read
The best Wi-Fi routers of 2024 Camryn Smith — 7 min read
Latest
-
Thursday, July 25, 2024
Worried about losing your signal? This is how to keep your satellite dish cleanDavid Anders — 6 min read
-
Tuesday, July 23, 2024
The best free TV and movie streaming services 2024Camryn Smith — 5 min read
-
Tuesday, July 23, 2024
Everything you need to know about internet speedsRobin Layton — 8 min read