What’s the difference between Mbps vs. MBps?
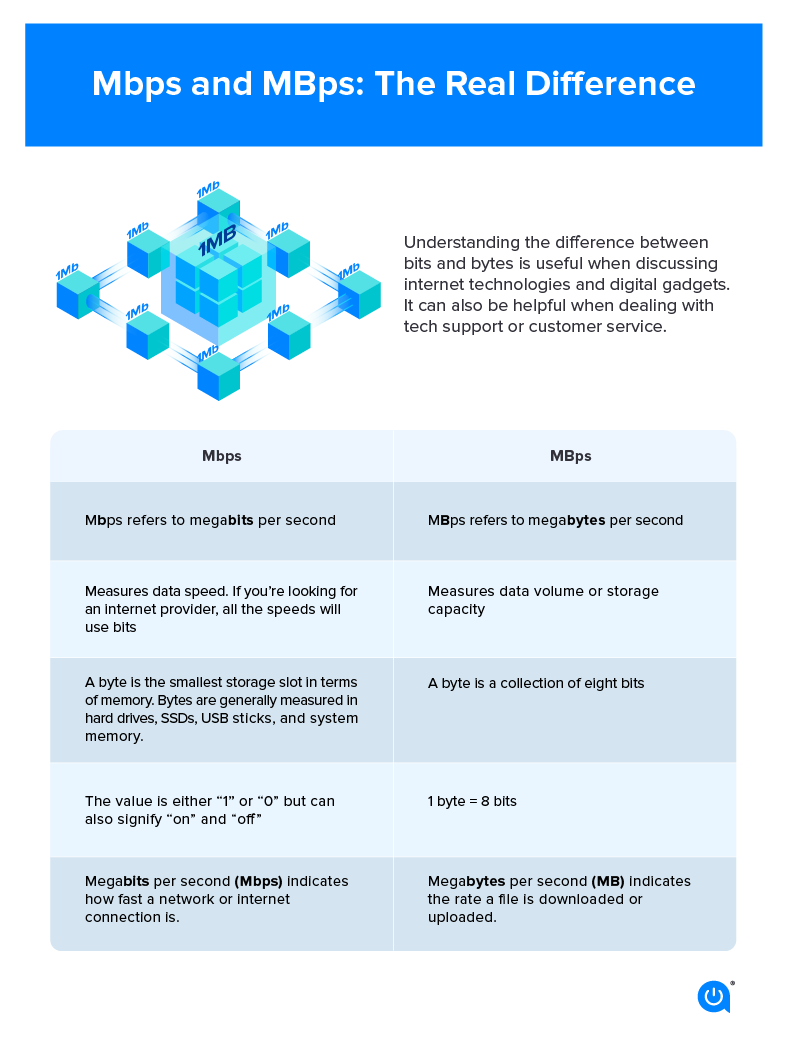
The main difference between the two terms comes down to bits vs. bytes. The first acronym, Mbps, with a lowercase “b,” refers to megabits per second, while the second, MBps, with a capital “B,” stands for megabytes per second.
“Megabits per second” (Mbps) measures download and upload speed, sometimes called bandwidth. For example, your favorite movie in HD may be 12 GB in size and to download it using a 10 Mbps internet plan would take nearly three hours. However, with a 500 Mbps internet plan, you’d have your movie in about three minutes.
The phrase “megabytes per second” (MBps) indicates the rate at which a file is downloaded or uploaded. For example, AT&T TV recommends 25 Mbps for streaming live TV, which does not involve downloading and saving a file. But when downloading a video game, the rate at which you download the file might be 100 MBps.
Bit vs. byte
For context, there are 8 bits in 1 byte. Basically, a bit measures data speed. In fact, all speeds from an internet service provider will be in bits, like 100 Mbps. A byte, however, measures storage capacity, so think of a pdf that is 4 MB in size.
A quick guide on data measurements
Don’t let these abbreviations trip you up! Here are some other common data measures that denote file size/data amounts, listed from smallest to largest:
- 1 Byte = 8 bits
- 1 Kilobyte (kB) = 1,024 Bytes
- 1 Megabyte (MB) = 1,024 Kilobytes
- 1 Gigabyte (GB or Gig) = 1,024 Megabytes
- 1 Terabyte (TB) = 1,024 Gigabytes
From bits to megabytes
1 Byte = 8 bits
1 Mbps = 1,000,000 bits = 125,000 Bytes
1 MB = 1,000,000 Bytes or 8,000,000 bits
A little bit for thought
Something to keep in mind to avoid confusion: “Megabyte” is interpreted differently depending on the field that uses it. For most of us, it means what we’ve defined here: a multiple of the byte for digital information. But, in the software development world, it is used to describe a computer’s memory as well as the size of a formatted floppy disk (remember those?).
How do Mbps and MBps affect my online activities?
As mentioned above, both Mbps and MBps come into play when you’re downloading things from the internet — everything from loading a webpage to downloading music and movies to streaming TV.
The time it takes to download will vary based on the size of the file and how fast of an internet connection you have. Other factors can affect download times as well, such as whether you are downloading using an Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi, or whether you are connected to residential or business internet.
But what if you already have high Mbps, but are still experiencing slow internet? If you have an appropriate download speed, but are still having trouble with activities such as gaming or video-chatting, then latency, not bandwidth, might be the problem. Learn the difference between bandwidth and latency and find out how to troubleshoot for this issue.
How long does it take to download a website, music and videos?
Keep in mind downloading bytes takes about 8X longer than downloading bits. For example, a 90 GB video game would take about 12 minutes on a 1 Gbps plan. Here’s approximately how long it would take to download the following media types at various connection speeds:
| Media | File size | 1 Mbps | 3 Mbps | 5 Mbps | 10 Mbps | 30 Mbps | 50 Mbps | 100 Mbps | 500 Mbps | 1 Gbps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Webpage | 1 MB | 8 seconds | 2 seconds | 1 second | <1 second | <1 second | <1 second | <1 second | <1 second | <1 second |
| MP3 song | 3 MB | 25 seconds | 8 seconds | 5 seconds | 2 seconds | <1 second | <1 second | <1 second | <1 second | <1 second |
| 10 minute SD video clip | 500 MB | 1 hour, 10 minutes | 23 minutes, 18 seconds | 14 minutes | 7 minutes | 2 minutes, 19 seconds | 1 minute, 23 seconds | 41 seconds | 8 seconds | 4 seconds |
| SD movie | 2 GB | 4 hours, 46 minutes | 1 hour, 35 minutes | 57 minutes, 15 second | 28 minutes, 37 seconds | 9 minutes, 32 seconds | 5 minutes, 43 seconds | 2 minutes, 51 seconds | 34 seconds | 17 second |
| HD movie | 12 GB | 28 hours, 38 minutes | 9 hours, 32 minutes | 5 hours, 43 minutes | 2 hours, 52 minutes | 57 minutes, 15 seconds | 34 minutes, 21 seconds | 17 minutes, 10 seconds | 3 minutes, 26 seconds | 1 minute, 43 seconds |
The bottom line: The larger the file size, the longer it takes to download
As you can see, the larger the file size the longer it will take to download at slower speeds. This is why it’s so important to consider your online activities when choosing an internet speed. A good thing to remember is that capital letters take longer to download than lowercase letters.
Take this 15-second quiz to see what speed you need!

Written by:
Camryn Smith
Cammy is a writer with Allconnect, growing her broadband industry knowledge for over a year on the internet marketplace. Her expertise lies in home internet and broadband service with a focus on providers, plans…
Read more
Edited by:
Robin LaytonEditor, Broadband Content
-
Featured
![30% of Americans say their internet is too slow. Here’s how to fix it]() 30% of Americans say their internet is too slow. Here’s how to fix it Joe Supan — 4 min read
30% of Americans say their internet is too slow. Here’s how to fix it Joe Supan — 4 min read -
Featured
![How much internet speed do I need?]() How much internet speed do I need? Joe Supan — 10 min read
How much internet speed do I need? Joe Supan — 10 min read -
Featured
![Upload vs. download speed: What’s the difference?]() Upload vs. download speed: What’s the difference? Joe Supan — 7 min read
Upload vs. download speed: What’s the difference? Joe Supan — 7 min read
Latest
-
Wednesday, April 24, 2024
Why do you need an Optical Terminal Network?Taylor Gadsden — 2 min read
-
Tuesday, April 23, 2024
Worried about losing your TV signal? This is how to keep your satellite dish cleanDavid Anders — 6 min read
-
Tuesday, April 23, 2024
How to change your Wi-Fi network passwordCamryn Smith — 2 min read






